In the rapidly evolving world of surveying, drones have emerged as a transformative tool, redefining how data is collected, analysed, and utilised across industries. These Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) have taken surveying to new heights—literally—by offering a faster, safer, and more efficient alternative to traditional methods. With their versatility and cutting-edge capabilities, drones are not just tools but a revolution in the making.
The Rise of Drone Technology in Surveying
The integration of drones into surveying practices has been driven by advancements in UAV technology and the demand for precision and efficiency. Modern drones are equipped with high-resolution cameras, LiDAR systems, and thermal imaging sensors, enabling them to capture detailed data from above with unprecedented accuracy.
From mapping vast landscapes to inspecting intricate structures, drones have proved indispensable for projects where traditional methods were either impractical or inefficient.
Key Benefits of Drone Technology in Surveying
1. Efficiency and Speed
One of the most significant advantages of drones is their ability to cover large areas quickly.
- Rapid Data Collection: Drones can survey hundreds of acres in a fraction of the time it would take a ground team.
- Reduced Project Timelines: Faster data acquisition means shorter project durations, leading to cost savings and quicker decision-making.
For instance, a drone can complete a topographical survey of a 100-acre site in a day—a task that might take weeks with conventional methods.
2. Enhanced Safety
Surveying often involves challenging environments, from steep cliffs to industrial facilities. Drones eliminate the need for human presence in hazardous areas.
- Minimising Risks: UAVs can access high-risk zones such as active mines, unstable structures, or disaster-hit regions without endangering personnel.
- Remote Monitoring: Operators can control drones from safe locations, ensuring safety while maintaining accuracy.
This capability has made drones indispensable for tasks such as inspecting wind turbines, bridges, and oil rigs.
3. High-Precision Data
Equipped with advanced sensors, drones deliver data that is both detailed and accurate.
- Aerial Photogrammetry: High-resolution cameras produce georeferenced images, which are used to create orthomosaic maps and 3D models.
- LiDAR Integration: LiDAR-equipped drones capture millions of data points to create precise digital terrain models, even penetrating vegetation canopies.
- Thermal Imaging: Drones with thermal cameras detect heat signatures, invaluable for infrastructure inspections and environmental surveys.
These capabilities provide a level of precision that surpasses traditional surveying methods.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in drone technology can be significant, the long-term savings are substantial.
- Reduced Labour Costs: Fewer personnel are required on-site, as drones handle much of the data collection autonomously.
- Lower Equipment Costs: Unlike heavy surveying equipment, drones are lightweight and versatile, often reducing the need for additional tools.
- Minimised Resource Use: Faster project completion translates to lower fuel and material usage, aligning with sustainability goals.
Applications of Drone Technology Across Sectors
1. Agriculture
Drones are revolutionising precision agriculture by providing farmers with actionable insights.
- Crop Health Monitoring: Multispectral cameras assess plant health and detect early signs of disease or nutrient deficiency.
- Irrigation Planning: Detailed elevation maps optimise water distribution, conserving resources.
- Yield Forecasting: Drones enable accurate predictions of harvest yields, helping farmers plan effectively.
2. Construction and Infrastructure
The construction industry relies heavily on drones for site surveys and progress monitoring.
- Pre-Construction Surveys: Detailed topographical data aids in site selection and project planning.
- Progress Tracking: Regular drone flights provide updates on construction milestones, ensuring timelines are met.
- Structural Inspections: From high-rise buildings to bridges, drones inspect structures for defects, saving time and reducing costs.
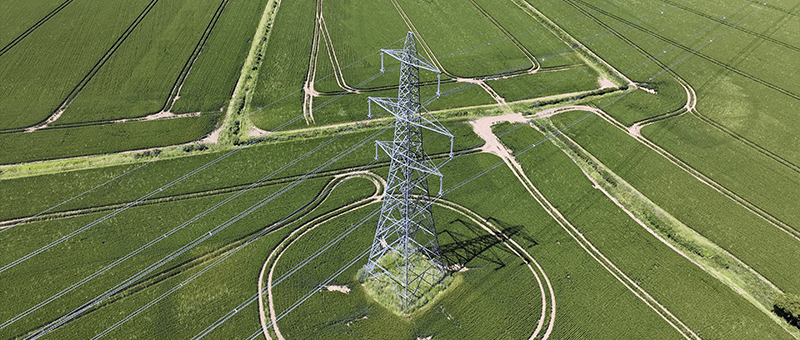
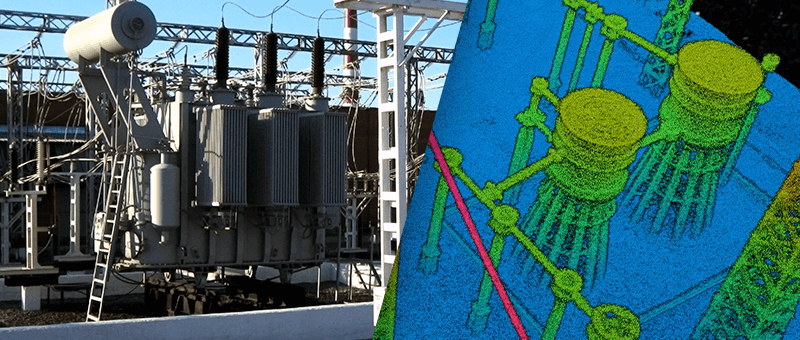
3. Energy and Utilities
In the energy sector, drones are used to inspect and maintain critical infrastructure.
- Wind Turbines: UAVs detect cracks and wear on blades, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Solar Panels: Thermal imaging identifies faults in panels, ensuring maximum energy output.
- Power Lines: Drones inspect power lines for damage or vegetation encroachment, enhancing reliability and safety.
4. Environmental Monitoring
Environmentalists leverage drones to track changes in ecosystems and manage conservation efforts.
- Wildlife Monitoring: Non-invasive aerial surveys track animal populations and movements.
- Habitat Mapping: High-resolution imaging provides insights into habitat conditions and changes over time.
- Erosion Control: Coastal surveys monitor erosion patterns, aiding in sustainable land management.
5. Emergency Response
Drones have become a vital tool in disaster management and search and rescue operations.
- Post-Disaster Surveys: UAVs map affected areas, providing real-time data for recovery efforts.
- Search and Rescue: Thermal imaging helps locate individuals in challenging conditions, such as dense forests or rubble.
Technological Innovations in Drone Surveying
The evolution of drone technology continues to push boundaries. Key innovations include:
- Autonomous Flight: Pre-programmed flight paths enable drones to operate with minimal human intervention.
- AI Integration: Artificial Intelligence enhances data analysis, identifying patterns and anomalies automatically.
- Swarm Technology: Coordinated fleets of drones can cover extensive areas simultaneously, improving efficiency.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its numerous advantages, drone technology in surveying is not without challenges.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Stringent airspace regulations often limit drone operations, particularly in urban areas.
- Weather Dependency: Adverse weather conditions can disrupt flights, delaying projects.
- Data Management: The vast amount of data generated by drones requires robust processing and storage solutions.
However, the future looks promising. Ongoing advancements in battery technology, AI, and regulatory frameworks are set to expand the capabilities and applications of drones in surveying.
Conclusion
Drone technology has undeniably revolutionised surveying, offering unparalleled efficiency, safety, and precision across various sectors. As these flying marvels continue to evolve, they are poised to become an even more integral part of surveying and beyond.
At Matrix Advanced Solutions, we embrace this innovation, integrating drones into our surveying practices to deliver exceptional results for our clients. Whether it’s mapping farmland, inspecting infrastructure, or supporting emergency response, our drone solutions are paving the way for a smarter, more sustainable future.